Area of a triangle
The triangle is one of the most important shapes in mathematics. In geometry, the triangle is a three-sided polygon that consists of three vertices and three edges. One of the most important properties of the triangle is the sum of all its internal angles is 180 degrees. If ABC is a triangle, then it is denoted as ∆ABC.
There are many sorts of triangles. Acute-angled. Obtuse-angled. Right-angled.
How to find the area of a triangle?
There are multiple triangles therefore ultimately there are many sorts of ways that you can use to calculate its area.
The most commonly used formula if a right-angled triangle is given is ½ x base x height.
What does a right-angled triangle look like?
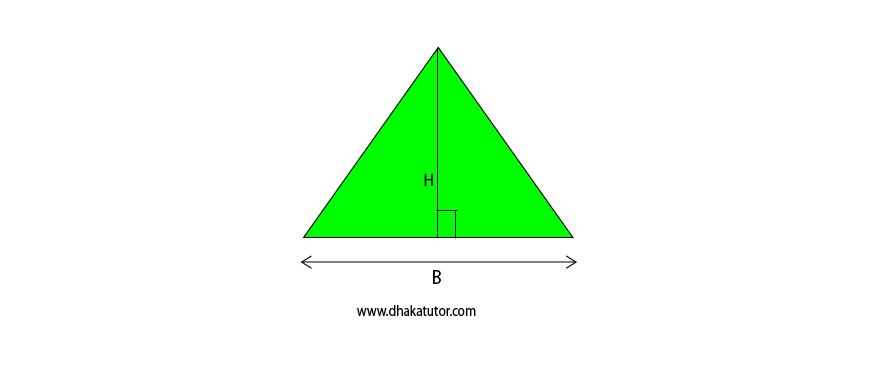
In the scenario given above, there are two right-angled triangles attached to each other. But they will be counted whole as an object. It is a two-dimensional shape. So how to calculate its area?
Suppose H= 10 and B =23. Putting it into the formula, ½ x 23 x 10 gives us 115 units squared.
Again, Suppose H= 11 and B =24. Putting it into the formula, ½ x 24 x 11 gives us 132 units squared.
Again, Suppose H= 16 and B =29. Putting it into the formula, ½ x 29 x 16 gives us 232 units squared.
Moving on.
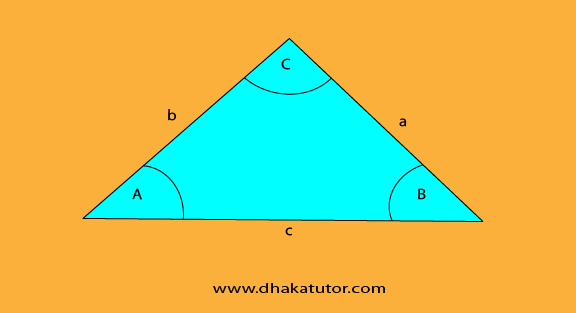
How to find the area of this type of triangle? There is a formula for everything. In this case, you have to use ½ x a x b x sin(c).
Suppose a=15 and b=19 and the given angle C is 62 degrees. What’s the area? Putting it into the formula ½ x 15 x 19 x sin(62) gives us 125.82 units squared.
Again, suppose a=16 and b=20 and the given angle C is 69 degrees. What’s the area? Putting it into the formula ½ x 16 x 20 x sin(69) gives us 149.37 units squared.
Just remember to keep your calculator in degree mode.