Structure and function of kidney
The shape of a kidney is like a bean but a size of a fist. There is a fibrous renal capsule around the kidney that covers it. It is there to support the soft structure of the kidney. On top of that, two more layers of fat provide good protection for the kidney.
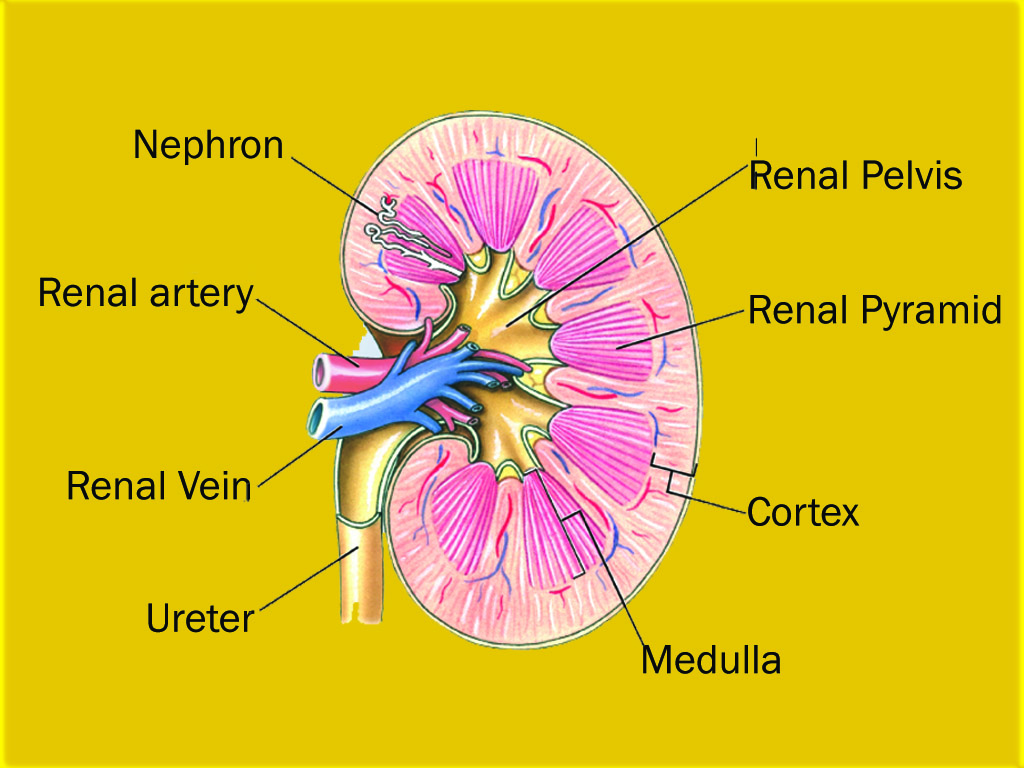
These four main kidney structures are the outer renal cortex, an inner renal medulla, a renal pelvis, and a nephron. The functions of kidneys are: it removes wastes from the body, eliminates drugs if there are any, releases hormone that helps to regulate the blood pressure of a person, it also controls the production of red blood cells in the body, balances body fluids present in the body, etc.
The kidney size is about 10 to 12 centimeters, around 5 inches.
'Nephron' is the functional unit of the kidney that uses filtration, reabsorption, secretion, and excretion to convert blood into urine that is later removed from the body.
Connective tissue holds the kidney in place and helps it to perform its task. Each kidney can contain about 1 million nephrons. Nephrons are the smallest parts of kidneys that are very important.
Kidneys can be damaged if diabetes or a person's blood pressure is too high. Kidney failure can also lead to death in most cases. It gets challenging to save a person whose kidneys are damaged.
They can live for a certain number of years; not more than. Apart from death, it can cause physical issues, pain, and other disorders.
Role of the kidney in excretion
Kidneys remove extra fluids and waste materials from our bodies through excretion. Kidneys filtrate the blood and purify it. The blood is again sent back. The main functions of the kidneys are:
- It helps in maintaining overall fluid balance.
- It filters waste materials from food.
- It purifies harmful chemicals and drugs.
- It creates hormones that help produce red blood cells
- It promotes bone health and regulates blood pressure.
- Kidneys can pump about 50 gallons or more amount of blood regularly.
A person can also survive with one kidney because a kidney alone can perform the work done by two kidneys. But a person with one kidney will be much weaker than a person with two kidneys. If a person’s both kidneys are damaged, they can transplant a kidney from a kidney donor who’s willing to donate.
This process is known as kidney transplantation, where a person can get a kidney from another person with two healthy kidneys. But the donor must be aware that they are donating, matching tissue, and check whether the donor has any diseases or other medical issues. If all these factors match, then a person is ready to donate.
Function of Kidney
Control of urine concentration
Urine is a liquid waste, a metabolism product produced inside all organisms. It has a few characteristics:
- It has the color of straw, and sometimes it looks transparent. It can also be described as yellow amber, which is a type of pale-yellow color. If a person drinks a lot of water, their urine color will be lighter, and if it looks dark yellow, it means the person is dehydrated and drinking less water regularly. If the urine seems red, it means it contains red blood cells due to medical issues.
- It has a mild odor due to the diet.
- The pH of urine is often affected by diet. The normal urine pH is around 4.6 to 8, with an average of around 6.0. It means that urine is alkaline in general.
- The range of normal urine density or specific gravity is around 0.001 to 0.035. it depends on the intake of food, or the diet followed.
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) is a hormone that is found in the bodies of all living organisms. It is produced by the pituitary gland, which increases the amount of water reabsorbed in the distal convoluted tubule of our bodies. ADH is a chemical that is produced in the brain. It causes kidneys to produce less water so that the amount of urine produced decreases. An increase in the ADH levels causes the kidneys to produce less water so that less urine is produced in an organism. Whereas when an organism's ADH level is low, less water is produced by the kidneys. Hence, the amount of urine produced is less.
The concentration of urine can surely be controlled by a lot of factors and habits, such as:
- The food or liquids we consume every day.
- The amount of water we drink.
- The diseases or other medical problems like diabetes, dehydration, etc.
- Out habits such as intake of drugs or consumption of alcohol.
Control of sodium in the blood
Controlling the amount of sodium in the blood means controlling the blood volume. Our brain monitors blood volume and sodium concentration continuously. The kidneys can detect if the blood volume or sodium concentration of the blood gets too high in the body. It is also sensed by the heart (that pumps blood to all body parts) and the blood vessels, arteries, veins, and capillaries that carry the blood throughout the entire body.
The amount of sodium in the blood is controlled by a hormone called aldosterone. It is produced in the adrenal glands. The aldosterone levels control the amount of sodium in the body by the kidneys. Kidneys then hold or pass sodium with the urine according to the need. The amount of sodium in the blood is regulated by the kidneys in the endocrine system. Foods that contain potassium such as:
- Sweet potatoes
- Potatoes
- Green vegetables
- Tomatoes
- Lower-sodium tomato sauce
- White beans
- Kidney beans
- Nonfat yogurt
- Oranges
- Bananas
- Cantaloupe.
These foods containing potassium are very healthy. Potassium in the diet helps to counter the effects of sodium. This may also help in lowering the body's blood pressure.
The high amount of sodium in the diet can be lowered by staying hydrated and drinking the right amount of water daily to fix dehydration.
Role of the kidney in Osmoregulation
In the process of Osmoregulation, the kidneys are one of the main organs that perform essential tasks. To maintain osmolarity, the kidneys filter blood and purify the blood.
It helps to keep osmoregulation and chemical homeostasis in the body. The kidneys are protected and surrounded by two layers of fat, making it easy for them to perform their blood.
It ensures that the soft inner part of the kidney is safe and provides insulation. Kidneys help in regulating the osmotic pressure of the organisms’ blood. It is done through two processes. One is filtration, and the other is purification. It is known as Osmoregulation.