Management is an ongoing, universal process. The successful use of the organization's materials (human and material) through the exercise of influence and control over a group of one or more people to accomplish a particular objective, according to Socrates. An important economic resource is a social mechanism.
The English term management (to handle) comes from the Latin or Italian maggiore (to train a horse), which means "to teach a man to grow." Has come to be associated with realization. Because of the presence of the society or the society involved, ‘management' has become one of the divisions of science.
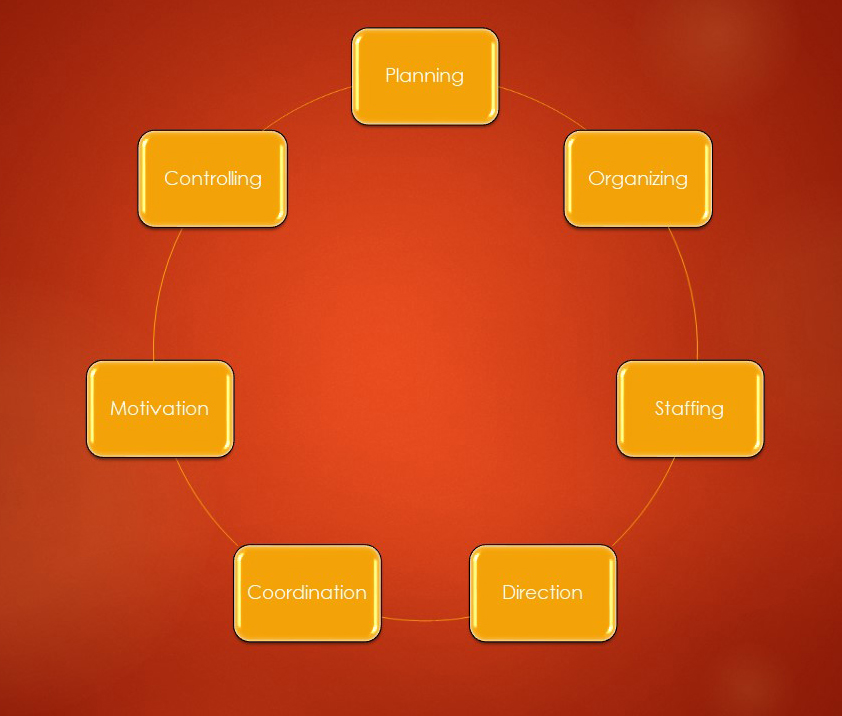
Basic functions of Management:
Plans are usually made based on experience, current surroundings, and the strengths, abilities, weaknesses, etc. of the organization concerned.
1. Planning - Planning is the most fundamental and first duty of management. The method of making plans in preparation for upcoming projects is known as planning.
All relevant matters must be prepared before undertaking any mission. The plan's goal is to determine where, where, what works, who will do them, and how they will be achieved. The agenda outlines the organization's goals and the plans, regulations, policies, services, and other elements needed to achieve them.
Plans are typically focused on experience, present circumstances, and the capabilities, skills, and shortcomings of the organization in question.
The optimal alternative is selected from a range of alternatives in preparation as part of the decision-making process. The highest degree of planning is used for simple and relevant matters. Middle and lower-level administrators devise their strategies in terms of these considerations.
2. Organizing - The organized organization of material and manpower assembled to accomplish an objective is referred to as organizing. The composition of the company is unique. Employees' tasks and roles are specifically allocated within the organization.
As a result, workers would be able to understand and fulfill their delegated tasks and obligations with ease. The company is a well-coordinated mix of personnel, infrastructure, machines, equipment, and workspace needed to meet the objectives.
3. Staffing - Staffing refers to the administrative tasks that are carried out to address a personnel shortfall in an organization's system.
In this situation, management is in charge of hiring workers for various positions, reviewing their duties, deciding pay and salaries, and so on, all by the job description.
It is impossible to perform administrative duties if the necessary personnel is not hired, and the hired personnel are not well trained to become skilled and experienced.
As a result, after establishing the hierarchical framework of management, provisions are made for the establishment of staff in this implementation.
4. Direction - The instructions, recommendations, or advice provided to workers at various levels of the corporate system to carry out the agenda implemented to meet pre-determined objectives. It is a vital factor that enables the boss to know exactly what he wants, where, how, and what to expect from his staff, among other things. Employees must have thorough descriptions of orders in easy-to-understand words for them to be understood. What to do: Train the workers and keep an eye on them and see how they are working to their full potential.
5. Coordination - Coordination is a method of team understanding in which different entities, organizations, and teams within an organization must execute their respective tasks to achieve the organization's key objectives. Since everyone's main goal is the same, it's critical to create coordination or consistency in their efforts. Otherwise, the targets' execution would be hampered. As a result, the organization's management coordination frequently harmonizes the role of workers working in various offices and divisions.
6. Motivation - Motivation is the management's responsibility of delivering motivation, motivation, and happiness to the organization's workers. Motivation is a phenomenon that piques an employee's interest in completing a job to achieve a certain objective. For encouragement, management implements a variety of financial and welfare schemes. Appropriate remuneration, work protection provisions, incidental allowances, opportunity to partake in decision-making, leisure plans, and so on are examples of these. Employee confidence, enthusiasm, and productivity all rise as a result of motivation. As a result, the workers develop a sense of harmony and cohesion, while also improving the consistency and productivity of the work.
7. Controlling - One of the most basic management functions is controlling. Regulation is the process of carrying out all of the organization's tasks according to the schedule. Control means the goals are met. The purpose of control is to ensure that the work is being done by the adopted schedule, given orders, and defined policies.
You May Also Like
What are the top most duties and responsibilities of property manager?